What Is Diffuse Hepatocellular Disease
What is diffuse hepatocellular disease. Infiltrative HCC has been described as diffuse HCC cirrhotomimetic-type HCC or cirrhosis-like HCC 7 8. Hepatocellular disease is a type of liver disease. It happens when fat builds up in the liver.
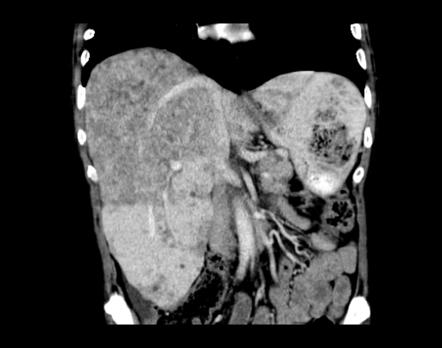
In severe cases this scarring can lead to liver failure. Diffuse hepatocellular problems are associated with fatty liver problems such as NASH or alcoholic liver problems. Ultrasonography has proven usefuI in evaluating the parenchymal struc- ture of the liver in animals- and therefore ultrasonogra-.
Send thanks to the doctor. When fatty liver develops in someone who drinks a lot of alcohol its known as alcoholic fatty liver disease. This is caused by a metabolic disease process that creates fatty vacuoles inside the liver.
Yellowish discoloration of the skin and eyes Abdominal pain Distension of the abdomen Severe itching of skin Dark or tea colored urine Pale stools Intermittent blood in the stools Extreme fatigue Nausea Loss of. Having small amounts of fat in your liver is normal but too much can become a health problem. Furthermore hepatocellular disease can be confirmed in the setting of indeterminate clinical and laboratory findings.
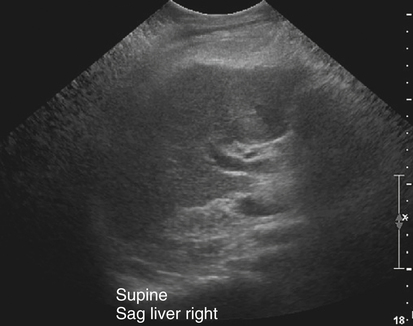
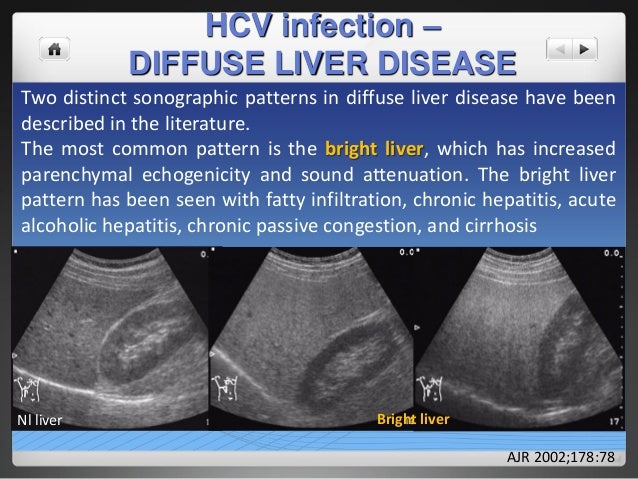
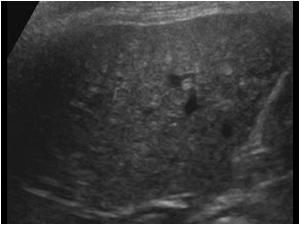
In this manner what is diffuse hepatocellular disease. Diffuse liver disease appears ultrasonographically as a change in liver echogenicity from normal when compared with the renal cortex or spleen. Hepatocellular carcinoma is a cancer that begins in the liver cells and is the most common of the primary liver cancers.
15 from fluid retention would cause ascites. Over a period of time the liver cell swill begin to die off with this disease. It is mostly caused by viral hepatitide infection or cirrhosis.
Fatty liver disease also known as hepatic steatosis is most often associated with alcoholism but it may occur in patients who are not heavy drinkers. Diffuse liver disease can be characterized as either hyperechoic due to fatty change steroid hepatopathy and cirrhosis or hypoechoic due to congestion suppurative hepatitis and lymphoma.
Diffuse liver disease appears ultrasonographically as a change in liver echogenicity from normal when compared with the renal cortex or spleen.
Hepatitis would cause a diffuse hepatocellular problem. The classic symptoms of diffuse hepatocellular liver disease include. It happens when fat builds up in the liver. Infiltrative HCC is characterized by the spread of minute tumor nodules throughout a hepatic lobe or the entire liver. Fatty liver disease also known as hepatic steatosis is most often associated with alcoholism but it may occur in patients who are not heavy drinkers. Diffuse hepatocellular problems are associated with fatty liver problems such as NASH or alcoholic liver problems. Diffuse liver disease can be characterized as either hyperechoic due to fatty change steroid. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of diffuse liver disease should be substantiated by biopsy and histopatho- logic evaluation. Having small amounts of fat in your liver is normal but too much can become a health problem.
Diffuse Liver Disease Diseases that affect the functional cells of the liver the hepatocytes are referred to as diffuse liver diseases. In severe cases this scarring can lead to liver failure. Diffuse Liver Disease Diseases that affect the functional cells of the liver the hepatocytes are referred to as diffuse liver diseases. Hepatopathy and cirrhosis or hypoechoic due to congestion suppurative hepatitis and lymphoma. With hepatocellular disease the liver is usually inflamed and will show signs of injury to the liver. It can be treated by liver transplant surgical resection Percutaneous ethanol injection transcatheter arterial chemoembolization etc. It happens when fat builds up in the liver.




























Post a Comment for "What Is Diffuse Hepatocellular Disease"