Eisenmenger Syndrome In Adults
Eisenmenger syndrome in adults. Abstract In Eisenmengers syndrome a central left-to-right shunt in the heart a congenital anomaly leads to pulmonary hypertension which subsequently causes the shunt to be reversed. Eisenmenger syndrome is associated with pulmonary arterial thrombus formation. What are predictors for death in adults with Eisenmenger syndrome ES.
This is a review of patients with Eisenmenger syndrome seen at the Toronto Congenital Cardiac Centre for Adults Canada. How common is Eisenmenger syndrome. Patients underwent a contrast-enhanced.
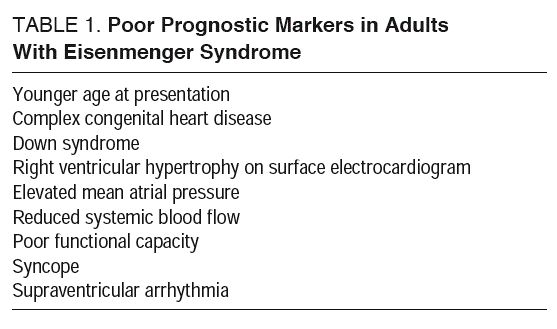
Patients with Eisenmenger syndrome ES have a higher mortality rate than patients with simple congenital heart disease CHD. The development of Eisenmenger syndrome in patients with complex congenital heart disease is associated with a 1012-fold increase in mortality. 10 The pathogenesis of PAH involves 3 major processes that contribute to narrowing of the pulmonary artery.
60 rows The exact number of people with Eisenmenger syndrome ES is. To determine factors associated with death in the era of advanced pulmonary vasodilator treatment we analyzed the characteristics of adult ES patients depending on underlying CHD. Eisenmenger syndrome is a rare condition that affects both the heart and the lungs.
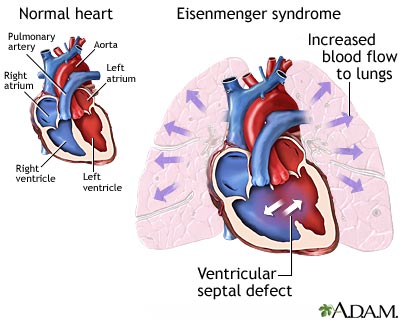
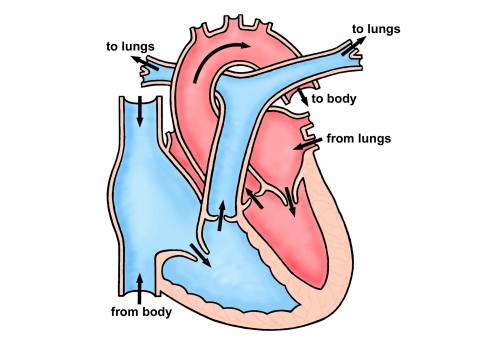
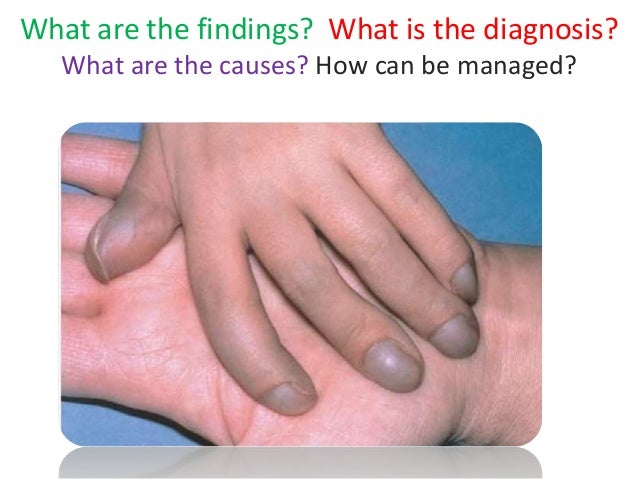
This particular birth defect is also called a congenital heart abnormality. Eisenmenger syndrome ES represents the most severe phenotype of pulmonary arterial hypertension PAH associated with congenital heart disease CHD and occurs in patients with large unrepaired shunts. Eisenmenger syndrome occurs as the result of a birth defect you are born with.
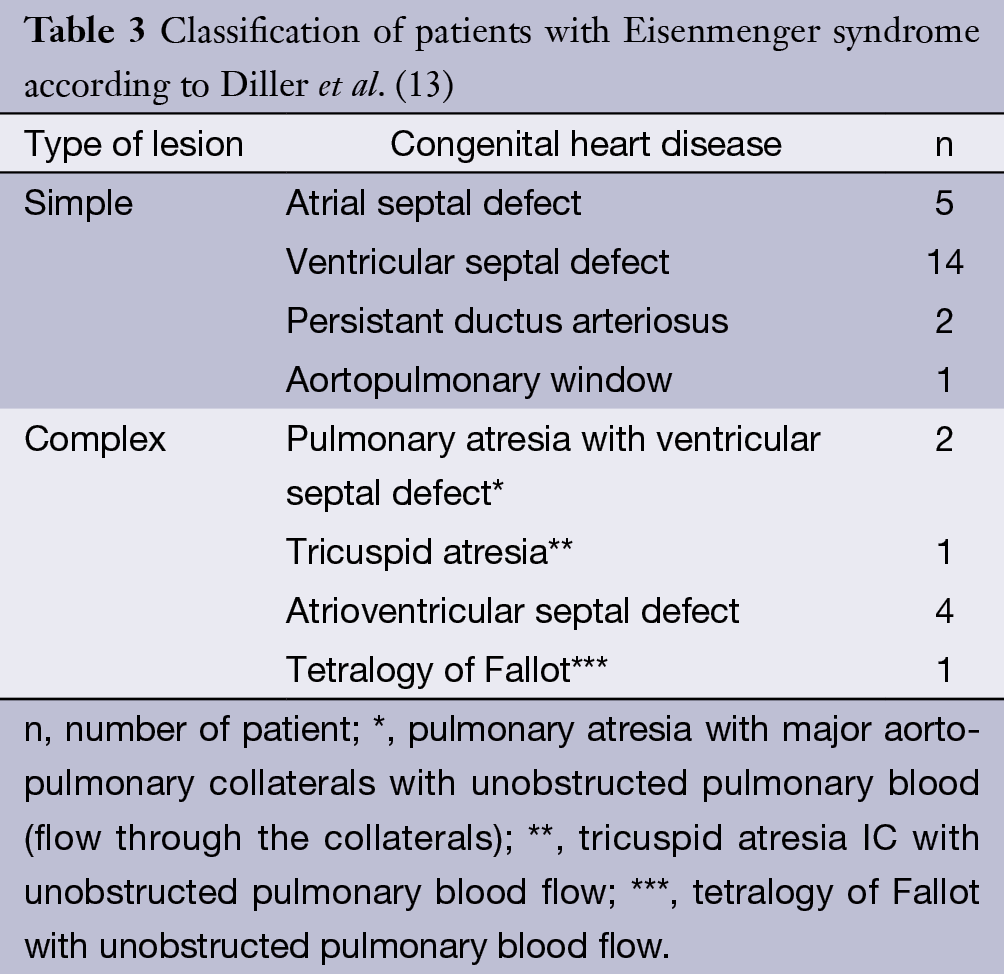
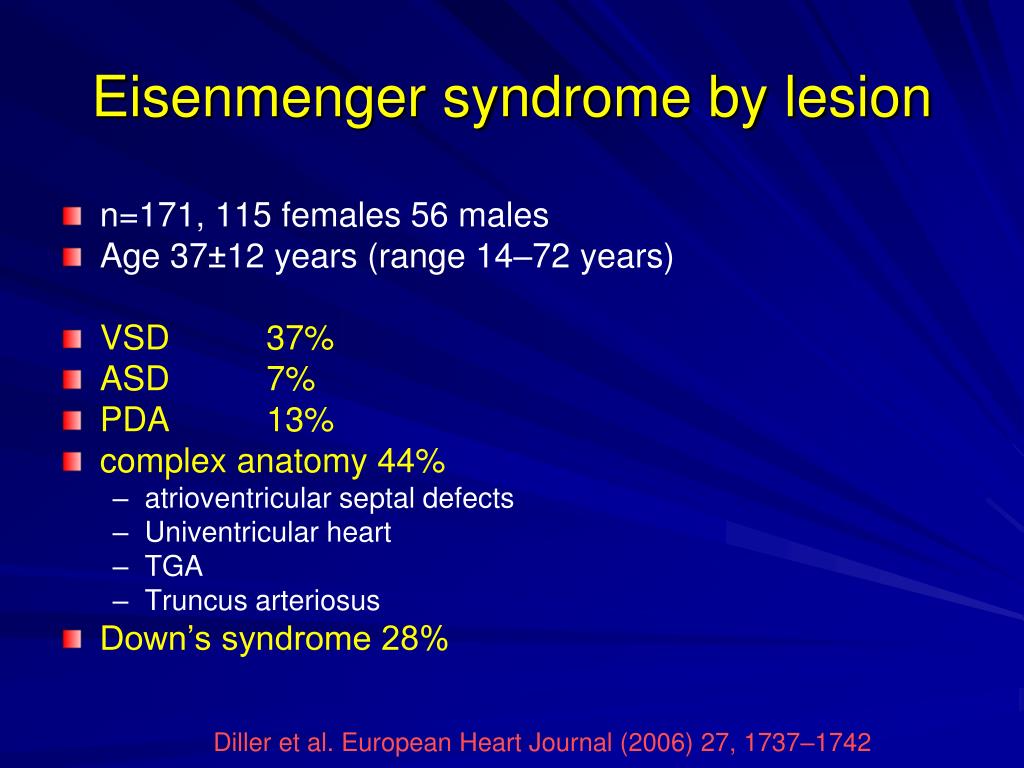
Patients were categorized as having pretricuspid lesions post-tricuspid lesions and mixed lesions combined pre- and post. A retrospective review of patients 16 years old followed at 11 international adult congenital heart disease ACHD clinics was performed. The number of people with congenital heart disease who develop the condition has decreased from 8.
Doctors most commonly diagnose Eisenmenger syndrome in people when they are young adults. Although the hemodynamic derangements and clinical history of adults with severe primary pulmonary hypertension have been well documented.
Patients with Eisenmenger syndrome ES have a higher mortality rate than patients with simple congenital heart disease CHD.
Abstract In Eisenmengers syndrome a central left-to-right shunt in the heart a congenital anomaly leads to pulmonary hypertension which subsequently causes the shunt to be reversed. The hypoxaemia resulting from a right-to-left shunt is compensated by an increase of the haemoglobin concentration due to a rise of the haematocrit. Due to the chronic slow progressive hypoxemia with central cyanosis adult patients with the Eisenmenger syndrome suffer from a complex and multisystemic disorder including. Both the prevalence and the determinants of pulmonary arterial thrombosis are unknown. How common is Eisenmenger syndrome. What are predictors for death in adults with Eisenmenger syndrome ES. Eisenmenger syndrome occurs as the result of a birth defect you are born with. To determine factors associated with death in the era of advanced pulmonary vasodilator treatment we analyzed the characteristics of adult ES patients depending on underlying CHD. The development of Eisenmenger syndrome in patients with complex congenital heart disease is associated with a 1012-fold increase in mortality.
What are predictors for death in adults with Eisenmenger syndrome ES. To determine factors associated with death in the era of advanced pulmonary vasodilator treatment we analyzed the characteristics of adult ES patients depending on underlying CHD. This particular birth defect is also called a congenital heart abnormality. In patients with Eisenmenger syndrome the shunt is bidirectional mainly from right-to-left low-velocity and with no associated murmur. This is a review of patients with Eisenmenger syndrome seen at the Toronto Congenital Cardiac Centre for Adults Canada. The hypoxaemia resulting from a right-to-left shunt is compensated by an increase of the haemoglobin concentration due to a rise of the haematocrit. The disease is characterized by high blood pressure and abnormal blood flow through the heart.

























31084-1.fp.png)





Post a Comment for "Eisenmenger Syndrome In Adults"