Fibrillin 1 Marfan Syndrome
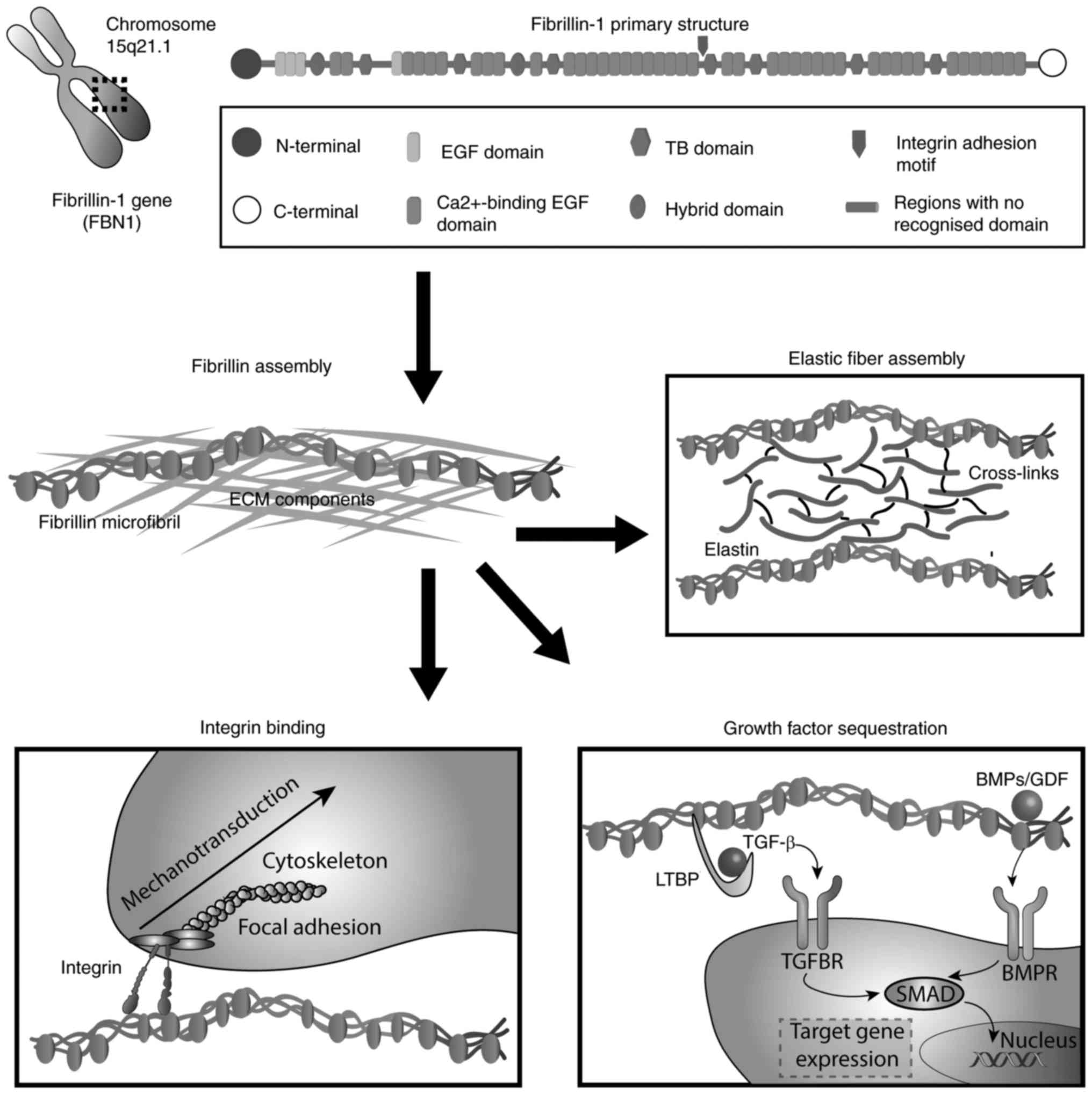
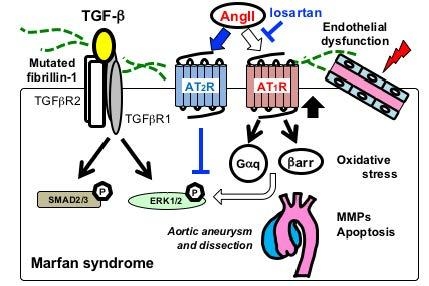
Fibrillin 1 marfan syndrome. FBN1 gene mutations that cause Marfan syndrome reduce the amount of fibrillin-1 produced by the cell alter the structure or stability of fibrillin-1 or impair the transport of fibrillin-1 out of the cell. MFS shows autosomal dominant transmission and an estimated incidence of 1 in 5000 live births. Marfan syndrome MFS is an inherited systemic disorder of the connective tissue caused by mutations in the fibrillin-1 FBN1 gene.
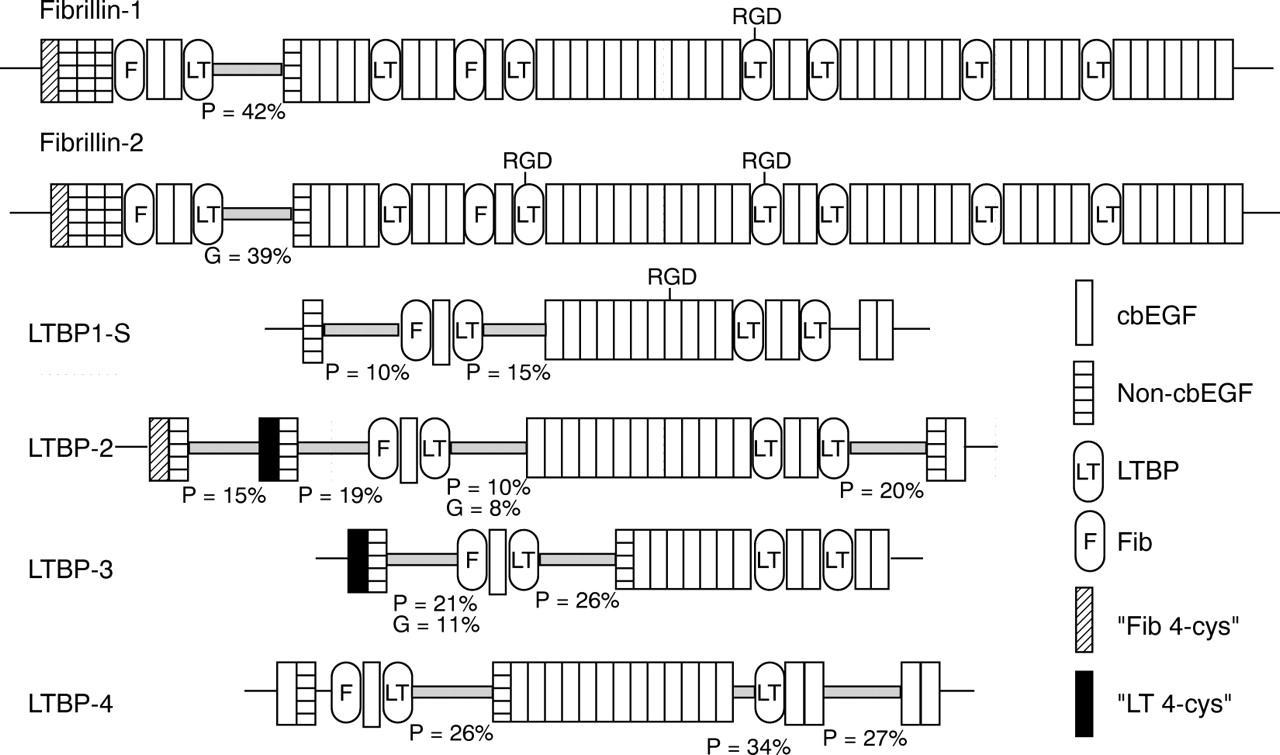
Mutations in the fibrillin-1 gene give rise to Marfan syndrome a connective tissue disorder with clinical complications in the cardiovascular skeletal ocular and other organ systems. Here we review the consequences of engineered Marfan syndrome mutations in fibrillin-1 at the protein cellular and organismal levels. This means that fibrillin-1 mutations were.
Steven Bassnett fourth from left and. Mutations in fibrillin-1 result in Marfan syndrome which affects the cardiovascular skeletal and ocular systems. Mutations in the fibrillin-1 gene give rise to Marfan syndrome a connective tissue disorder with clinical complications in the cardiovascular skeletal ocular and other organ systems.
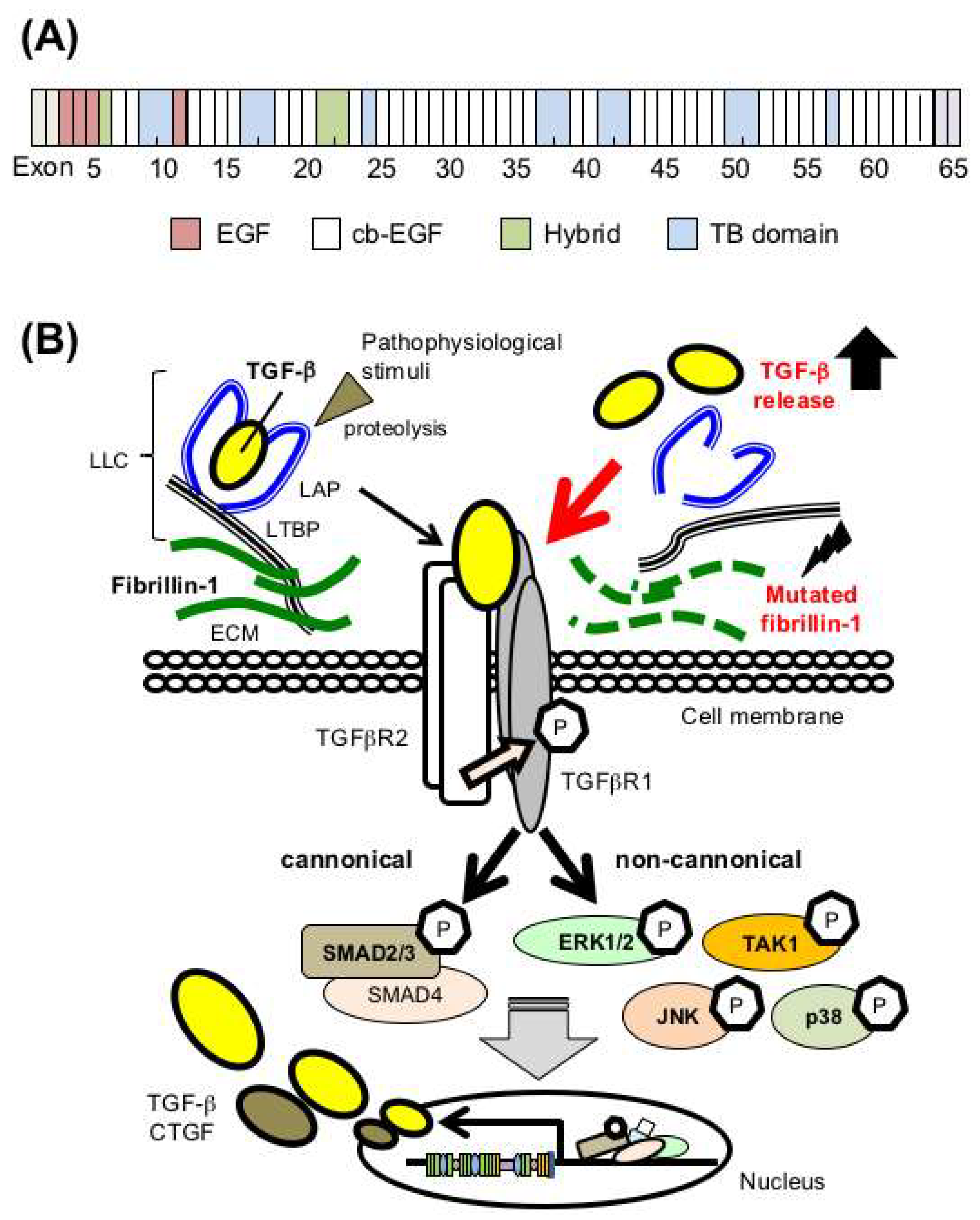
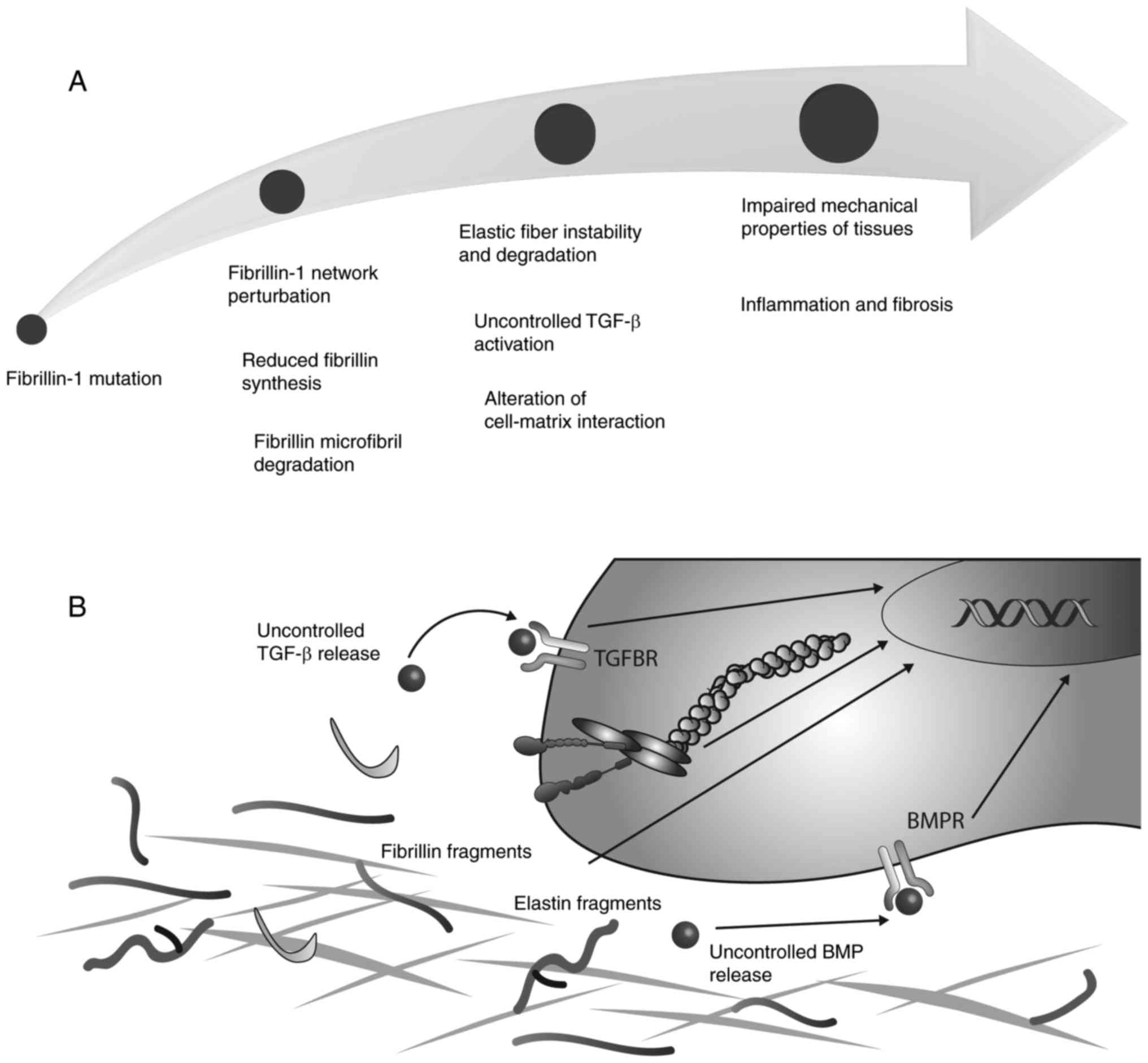
The multiorgan involvement and wide spectrum of associated phenotypes highlights the complex pathogenesis underlying Marfan syndrome. To our knowledge this sequence variant has been reported as a polymorphism rs113602180 but it is the first report identifying it as the genetic cause of Marfan syndrome. 8 FBN1 mutations have been shown to increase the susceptibility of fibrillin-1 to proteolysis in vitro leading to fragmentation of microfibrils.
Marfan syndrome has been linked to more than 3000 fibrillin-1 mutations. A recurrent fibrillin-1 mutation in severe early onset Marfan syndrome. In 1997 astudy of 60 Marfans found that only 28 of the people with the disorder had fibrillin-1 mutations.
Sureka D1 Stheneur C2 Odent S3 Arno G4 Murphy D5 Bernstein JA1. Fibrillin-1 also affects levels of another protein that helps control how you grow. In the eye the mutations weaken the zonule fibers to the point of breaking and letting go of the lens a condition called ectopia lentis.
That fibrillin-1 mutations cause Marfan syndrome. People with Marfan syndrome have increased risk of glaucoma cataract and high myopia.
FBN1 gene mutations that cause Marfan syndrome reduce the amount of fibrillin-1 produced by the cell alter the structure or stability of fibrillin-1 or impair the transport of fibrillin-1 out of the cell.
Yet studies of people with Marfan syndrome consistently show thata large percentage of them are not found to have any fibrillin-1 mutations. Fibrillin-1 also affects levels of another protein that helps control how you grow. 8 FBN1 mutations have been shown to increase the susceptibility of fibrillin-1 to proteolysis in vitro leading to fragmentation of microfibrils. In the eye the mutations weaken the zonule fibers to the point of breaking and letting go of the lens a condition called ectopia lentis. A recurrent fibrillin-1 mutation in severe early onset Marfan syndrome. Steven Bassnett fourth from left and. In 1997 astudy of 60 Marfans found that only 28 of the people with the disorder had fibrillin-1 mutations. FBN1 gene mutations that cause Marfan syndrome reduce the amount of fibrillin-1 produced by the cell alter the structure or stability of fibrillin-1 or impair the transport of fibrillin-1 out of the cell. That fibrillin-1 mutations cause Marfan syndrome.
Yet studies of people with Marfan syndrome consistently show thata large percentage of them are not found to have any fibrillin-1 mutations. The effect of FBN1 mutation type on the severity of cardiovascular manifestations in patients with Marfan syndrome MFS has been reported with disparity results. That fibrillin-1 mutations cause Marfan syndrome. People with Marfan syndrome have increased risk of glaucoma cataract and high myopia. In the eye the mutations weaken the zonule fibers to the point of breaking and letting go of the lens a condition called ectopia lentis. 6 FBN1 mutations are present in 90 of patients with Marfan syndrome. We hypothesize that this de novo novel missense FBN1 mutation disrupts fibrillin-1 function and is probably involved in the development of Marfan syndrome in this patient.








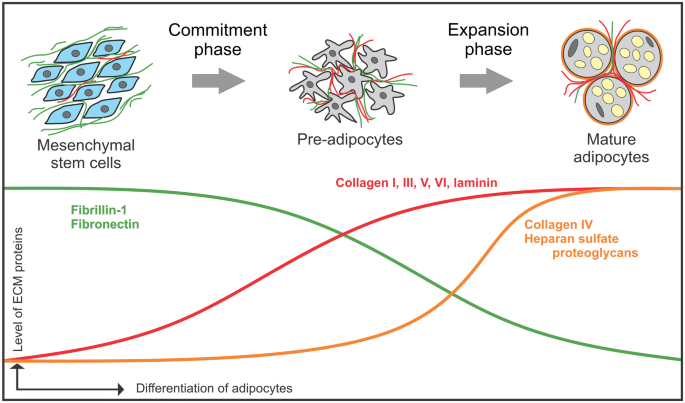

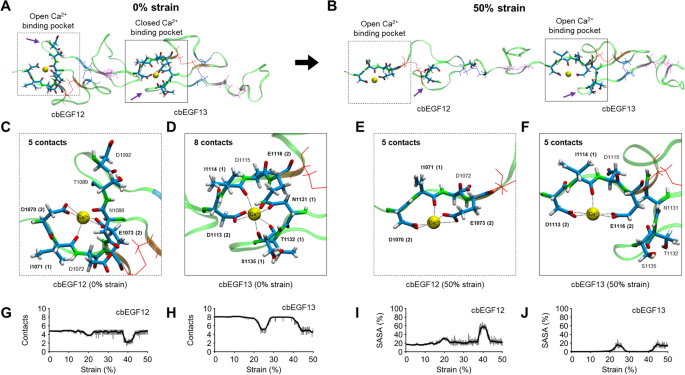




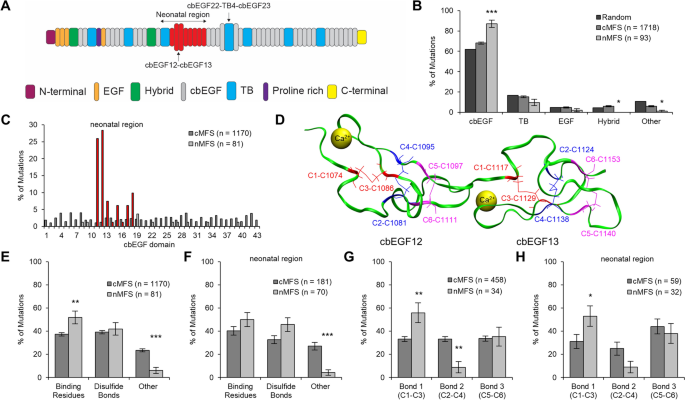




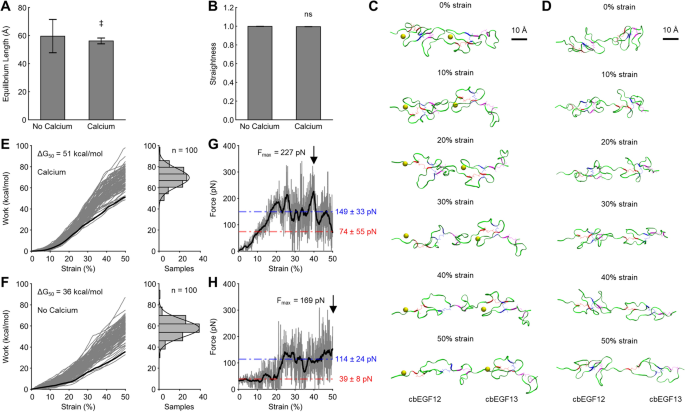








Post a Comment for "Fibrillin 1 Marfan Syndrome"